Delving into the realm of average health insurance cost unveils a complex web of factors and considerations that impact individuals and families alike. From demographics to lifestyle choices, the interplay of elements in determining insurance premiums is both fascinating and crucial in today's healthcare landscape.
As we navigate through the intricacies of health insurance costs, a clearer picture emerges of the various types of plans available, strategies to mitigate expenses, and the evolving trends that shape the future of insurance pricing.
Factors Affecting Average Health Insurance Cost
When it comes to determining the average cost of health insurance, several key factors come into play. These factors can significantly influence the premiums individuals pay for their health coverage.
Demographics
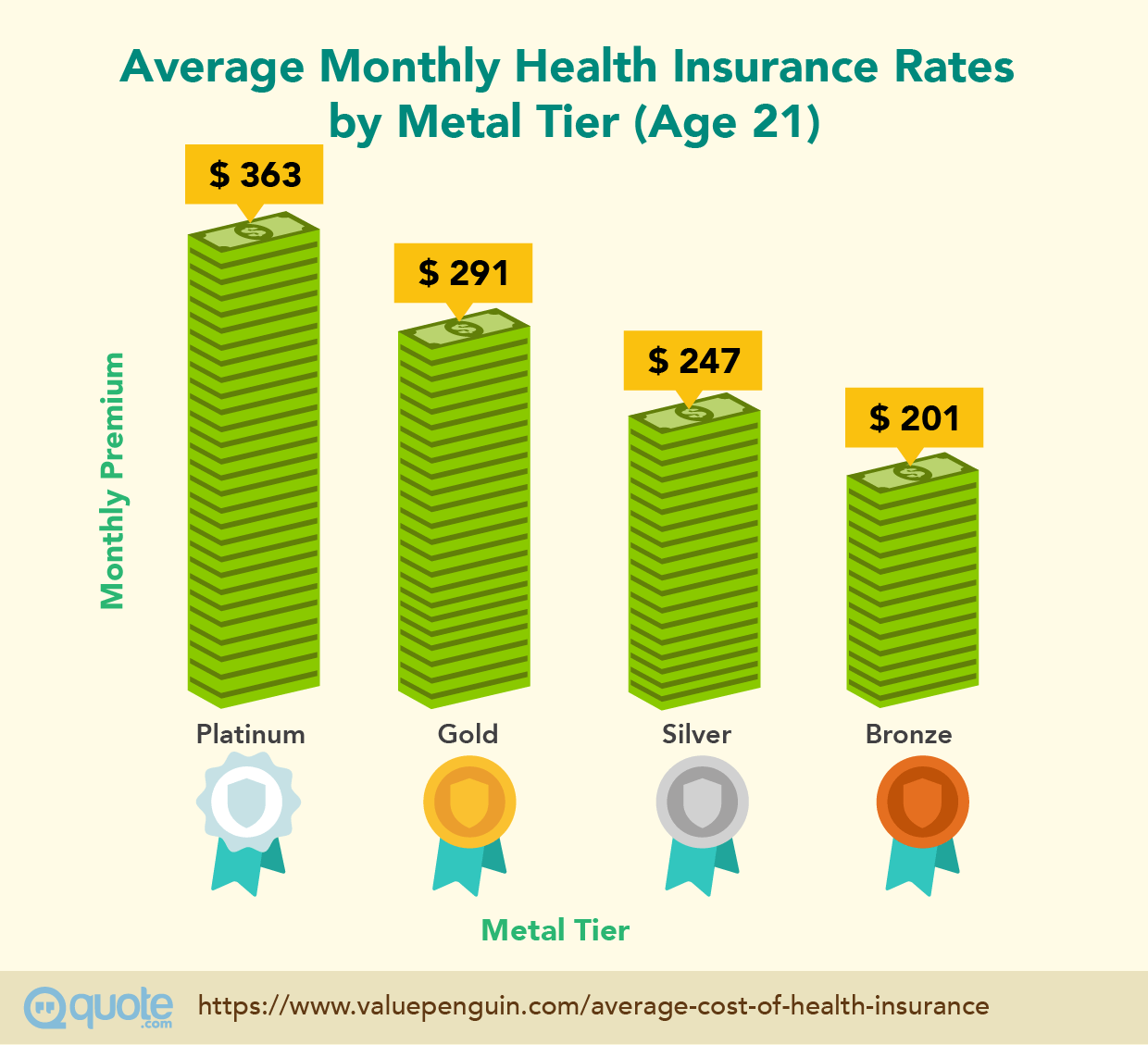
Demographics play a crucial role in determining health insurance costs. Factors such as age and location can have a significant impact on how much individuals pay for their health coverage. Generally, older individuals tend to pay higher premiums compared to younger individuals.
Additionally, individuals living in regions with higher healthcare costs may also face higher insurance premiums.
Lifestyle Choices
Individual lifestyle choices can also impact health insurance premiums. For example, individuals who smoke or lead sedentary lifestyles may face higher insurance costs due to the increased health risks associated with these habits. On the other hand, individuals who maintain a healthy lifestyle may be eligible for lower insurance premiums.
Pre-Existing Conditions
Having pre-existing conditions can also impact health insurance costs. Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer may lead to higher premiums as individuals with these conditions are considered higher risk by insurance companies. In some cases, individuals with pre-existing conditions may even be denied coverage or offered limited coverage options.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans come in various types, each with its own set of premiums, deductibles, and coverage. Understanding the differences between these plans is crucial in choosing the right one for your needs.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs require members to select a primary care physician (PCP) and receive referrals for specialist care. Premiums for HMOs are typically lower than other plans, but they have higher out-of-pocket costs and limited provider networks.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers without the need for referrals. While premiums are higher than HMOs, PPOs provide more coverage options and lower out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
High-Deductible Health Plans
High-deductible health plans have lower premiums but higher deductibles compared to other plans. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to help cover out-of-pocket expenses. These plans are ideal for individuals who are generally healthy and do not require frequent medical care.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Employer-sponsored health insurance plays a significant role in determining costs for many individuals. Employers often negotiate group rates with insurance companies, resulting in lower premiums for employees. However, the coverage and out-of-pocket costs may vary depending on the employer's chosen plan.
Strategies to Lower Health Insurance Costs
Managing health insurance costs can be challenging, but there are several strategies individuals can implement to reduce expenses and make healthcare more affordable.
Benefits of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are a valuable tool for managing healthcare costs. These accounts allow individuals to set aside pre-tax dollars specifically for medical expenses. By contributing to an HSA, individuals can lower their taxable income and pay for qualified medical expenses, such as deductibles and copayments, with tax-free funds.
Wellness Programs and Preventative Care
Participating in wellness programs and prioritizing preventative care can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of chronic conditions and costly medical treatments. Many health insurance plans offer incentives for engaging in wellness activities, such as gym memberships or discounted premiums for meeting health goals.
Negotiating Techniques to Lower Premiums
When it comes to lowering health insurance premiums, negotiation can be a powerful tool. Individuals can explore different insurance providers, compare rates, and leverage competing offers to negotiate better deals. Additionally, reviewing and adjusting coverage options based on changing healthcare needs can help individuals find more affordable plans without sacrificing necessary benefits.
Trends in Average Health Insurance Costs
Over the past decade, there has been a steady increase in average health insurance costs. Factors such as rising healthcare expenses, increased utilization of medical services, and an aging population have contributed to this upward trend.One of the significant impacts on insurance pricing has been healthcare reforms, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which aimed to increase access to healthcare for millions of Americans.
While the ACA brought about positive changes, such as coverage for pre-existing conditions and essential health benefits, it also led to higher premiums for some individuals due to mandated coverage requirements.Advancements in medical technology have also played a role in driving up insurance costs.
While these advancements have improved the quality of care and treatment options, they have also increased the overall cost of healthcare services. New treatments, medications, and procedures often come with a hefty price tag, which insurers pass on to consumers through higher premiums.Looking ahead, projected changes in health insurance costs indicate a continued increase in premiums.
Factors such as inflation, changes in healthcare policies, and the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic are expected to contribute to rising insurance costs in the future.
Impact of Aging Population
The aging population is a key driver of increasing health insurance costs. As individuals grow older, they typically require more medical services and treatments, leading to higher healthcare expenses. This demographic shift puts pressure on insurers to cover the costs associated with an aging population, resulting in higher premiums for all policyholders.
Technological Innovations in Healthcare
Advancements in medical technology, such as precision medicine, telemedicine, and wearable devices, have the potential to improve health outcomes and patient care. However, these innovations often come with a hefty price tag, which can drive up insurance costs. Insurers must factor in the cost of covering new technologies and treatments when setting premium rates, ultimately impacting the overall cost of health insurance for consumers.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the exploration of average health insurance costs sheds light on the multifaceted nature of this essential aspect of healthcare. By understanding the factors at play, individuals can make informed decisions to navigate the complexities of insurance pricing and secure their well-being in the face of rising healthcare costs.
FAQ Section
What are the key factors that influence average health insurance costs?
The key factors include demographics, lifestyle choices, pre-existing conditions, and the type of health insurance plan chosen.
How can individuals lower their health insurance costs?
Individuals can reduce costs by utilizing health savings accounts, participating in wellness programs, and negotiating with insurance providers.
What are the trends in average health insurance costs over the past decade?
Over the past decade, there has been a steady increase in health insurance costs due to factors such as healthcare reforms and advancements in medical technology.














